EIG Eigendecomposition of a Matrix
Section: Transforms/Decompositions
Usage
Computes the eigendecomposition of a square matrix. Theeig function
has several forms. The first returns only the eigenvalues of the matrix:
s = eig(A)
The second form returns both the eigenvectors and eigenvalues as two matrices (the eigenvalues are stored in a diagonal matrix):
[V,D] = eig(A)
where D is the diagonal matrix of eigenvalues, and V is the
matrix of eigenvectors.
Eigenvalues and eigenvectors for asymmetric matrices A normally
are computed with balancing applied. Balancing is a scaling step
that normaly improves the quality of the eigenvalues and eigenvectors.
In some instances (see the Function Internals section for more details)
it is necessary to disable balancing. For these cases, two additional
forms of eig are available:
s = eig(A,'nobalance'),
which computes the eigenvalues of A only, and does not balance
the matrix prior to computation. Similarly,
[V,D] = eig(A,'nobalance')
recovers both the eigenvectors and eigenvalues of A without balancing.
Note that the 'nobalance' option has no affect on symmetric matrices.
FreeMat also provides the ability to calculate generalized eigenvalues
and eigenvectors. Similarly to the regular case, there are two forms
for eig when computing generalized eigenvector (see the Function
Internals section for a description of what a generalized eigenvector is).
The first returns only the generalized eigenvalues of the matrix
pair A,B
s = eig(A,B)
The second form also computes the generalized eigenvectors, and is accessible via
[V,D] = eig(A,B)
Function Internals
Recall thatv is an eigenvector of A with associated eigenvalue
d if
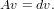
This decomposition can be written in matrix form as
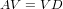
where
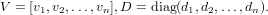
The eig function uses the LAPACK class of functions GEEVX
to compute the eigenvalue decomposition for non-symmetric
(or non-Hermitian) matrices A. For symmetric matrices, SSYEV
and DSYEV are used for float and double matrices (respectively).
For Hermitian matrices, CHEEV and ZHEEV are used for complex
and dcomplex matrices.
For some matrices, the process of balancing (in which the rows and
columns of the matrix are pre-scaled to facilitate the search for
eigenvalues) is detrimental to the quality of the final solution.
This is particularly true if the matrix contains some elements on
the order of round off error. See the Example section for an example.
A generalized eigenvector of the matrix pair A,B is simply a
vector v with associated eigenvalue d such that
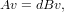
where B is a square matrix of the same size as A. This
decomposition can be written in matrix form as
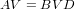
where
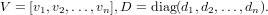
For general matrices A and B, the GGEV class of routines are
used to compute the generalized eigendecomposition. If howevever,
A and B are both symmetric (or Hermitian, as appropriate),
Then FreeMat first attempts to use SSYGV and DSYGV for float
and double arguments and CHEGV and ZHEGV for complex
and dcomplex arguments (respectively). These routines requires
that B also be positive definite, and if it fails to be, FreeMat
will revert to the routines used for general arguments.
Example
Some examples of eigenvalue decompositions. First, for a diagonal matrix, the eigenvalues are the diagonal elements of the matrix.
--> A = diag([1.02f,3.04f,1.53f])
A =
1.0200 0 0
0 3.0400 0
0 0 1.5300
--> eig(A)
ans =
1.0200
1.5300
3.0400
Next, we compute the eigenvalues of an upper triangular matrix, where the eigenvalues are again the diagonal elements.
--> A = [1.0f,3.0f,4.0f;0,2.0f,6.7f;0.0f,0.0f,1.0f]
A =
1.0000 3.0000 4.0000
0 2.0000 6.7000
0 0 1.0000
--> eig(A)
ans =
1
2
1
Next, we compute the complete eigenvalue decomposition of a random matrix, and then demonstrate the accuracy of the solution
--> A = float(randn(2))
A =
0.0501 0.1608
2.1808 -2.4972
--> [V,D] = eig(A)
V =
0.7754 -0.0599
0.6314 0.9982
D =
0.1811 0
0 -2.6282
--> A*V - V*D
ans =
1.0e-07 *
1.0431 -0.2980
-1.5646 0
Now, we consider a matrix that requires the nobalance option to compute the eigenvalues and eigenvectors properly. Here is an example from MATLAB's manual.
--> B = [3,-2,-.9,2*eps;-2,4,1,-eps;-eps/4,eps/2,-1,0;-.5,-.5,.1,1]
B =
3.0000 -2.0000 -0.9000 0.0000
-2.0000 4.0000 1.0000 -0.0000
-0.0000 0.0000 -1.0000 0
-0.5000 -0.5000 0.1000 1.0000
--> [VB,DB] = eig(B)
VB =
0.6153 -0.4176 -0.0000 -0.1530
-0.7881 -0.3261 -0.0000 0.1346
-0.0000 -0.0000 0.0000 -0.9790
0.0189 0.8481 1.0000 -0.0097
DB =
5.5616 0 0 0
0 1.4384 0 0
0 0 1.0000 0
0 0 0 -1.0000
--> B*VB - VB*DB
ans =
0.0000 -0.0000 -0.0000 0.0000
-0.0000 -0.0000 0.0000 0.0000
-0.0000 -0.0000 -0.0000 0
-0.0000 0.0000 0 -0.1081
--> [VN,DN] = eig(B,'nobalance')
VN =
0.6153 -0.4176 0.0000 -0.1528
-0.7881 -0.3261 0.0000 0.1345
-0.0000 -0.0000 -0.0000 -0.9781
0.0189 0.8481 -1.0000 0.0443
DN =
5.5616 0 0 0
0 1.4384 0 0
0 0 1.0000 0
0 0 0 -1.0000
--> B*VN - VN*DN
ans =
1.0e-16 *
8.8818 -1.1102 -1.6722 -1.1102
-8.8818 2.7756 0.1811 0.8327
0.1718 0.0154 0.0663 0
-0.6939 0 0 0.8327
