PLUS Addition Operator
Section: Mathematical Operators
Usage
Adds two numerical arrays (elementwise) together. There are two forms for its use, both with the same general syntax:y = a + b
where a and b are n-dimensional arrays of numerical type. In the
first case, the two arguments are the same size, in which case, the
output y is the same size as the inputs, and is the element-wise the sum
of a and b. In the second case, either a or b is a scalar,
in which case y is the same size as the larger argument,
and is the sum of the scalar added to each element of the other argument.
The rules for manipulating types has changed in FreeMat 4.0. See typerules
for more details.
Function Internals
There are three formulae for the addition operator, depending on the sizes of the three arguments. In the most general case, in which the two arguments are the same size, the output is computed via:
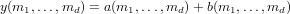
If a is a scalar, then the output is computed via
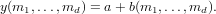
On the other hand, if b is a scalar, then the output is computed via
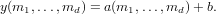
Examples
Here are some examples of using the addition operator. First, a straight-forward usage of the plus operator. The first example is straightforward:--> 3 + 8 ans = 11
Next, we add a scalar to a vector of values:
--> 3.1 + [2,4,5,6,7]
ans =
5.1000 7.1000 8.1000 9.1000 10.1000
With complex values
--> a = 3 + 4*i a = 3.0000 + 4.0000i --> b = a + 2 b = 5.0000 + 4.0000i
Finally, the element-wise version:
--> a = [1,2;3,4] a = 1 2 3 4 --> b = [2,3;6,7] b = 2 3 6 7 --> c = a + b c = 3 5 9 11
