HERMITIAN Matrix Hermitian (Conjugate Transpose) Operator
Section: Mathematical Operators
Usage
Computes the Hermitian of the argument (a 2D matrix). The syntax for its use isy = a';
where a is a M x N numerical matrix. The output y is a numerical matrix
of the same type of size N x M. This operator is the conjugating transpose,
which is different from the transpose operator .' (which does not
conjugate complex values).
Function Internals
The Hermitian operator is defined simply as
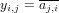
where y_ij is the element in the ith row and jth column of the output matrix y.
Examples
A simple transpose example:--> A = [1,2,0;4,1,-1] A = 1 2 0 4 1 -1 --> A' ans = 1 4 2 1 0 -1
Here, we use a complex matrix to demonstrate how the Hermitian operator conjugates the entries.
--> A = [1+i,2-i] A = 1.0000 + 1.0000i 2.0000 - 1.0000i --> A.' ans = 1.0000 + 1.0000i 2.0000 - 1.0000i
