DOTPOWER Element-wise Power Operator
Section: Mathematical Operators
Usage
Raises one numerical array to another array (elementwise). There are three operators all with the same general syntax:y = a .^ b
The result y depends on which of the following three situations applies to the arguments a and b:
-
ais a scalar,bis an arbitraryn-dimensional numerical array, in which case the output isaraised to the power of each element ofb, and the output is the same size asb. -
ais ann-dimensional numerical array, andbis a scalar, then the output is the same size asa, and is defined by each element ofaraised to the powerb. -
aandbare bothn-dimensional numerical arrays of \emph{the same size}. In this case, each element of the output is the corresponding element ofaraised to the power defined by the corresponding element ofb.
typerules
for more details.
Function Internals
There are three formulae for this operator. For the first form
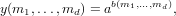
and the second form
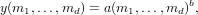
and in the third form
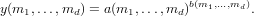
Examples
We demonstrate the three forms of the dot-power operator using some simple examples. First, the case of a scalar raised to a series of values.--> a = 2 a = 2 --> b = 1:4 b = 1 2 3 4 --> c = a.^b c = 2 4 8 16
The second case shows a vector raised to a scalar.
--> c = b.^a c = 1 4 9 16
The third case shows the most general use of the dot-power operator.
--> A = [1,2;3,2]
A =
1 2
3 2
--> B = [2,1.5;0.5,0.6]
B =
2.0000 1.5000
0.5000 0.6000
--> C = A.^B
C =
1.0000 2.8284
1.7321 1.5157
