EXP Exponential Function
Section: Mathematical Functions
Usage
Computes theexp function for its argument. The general
syntax for its use is
y = exp(x)
where x is an n-dimensional array of numerical type.
Integer types are promoted to the double type prior to
calculation of the exp function. Output y is of the
same size and type as the input x, (unless x is an
integer, in which case y is a double type).
Function Internals
Mathematically, theexp function is defined for all real
valued arguments x as
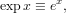
where
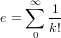
and is approximately 2.718281828459045 (returned by the function
e). For complex values
z, the famous Euler formula is used to calculate the
exponential

Example
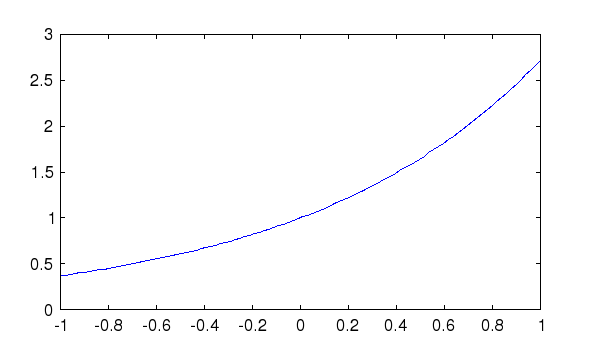
The following piece of code plots the real-valuedexp
function over the interval [-1,1]:
--> x = linspace(-1,1); --> plot(x,exp(x))
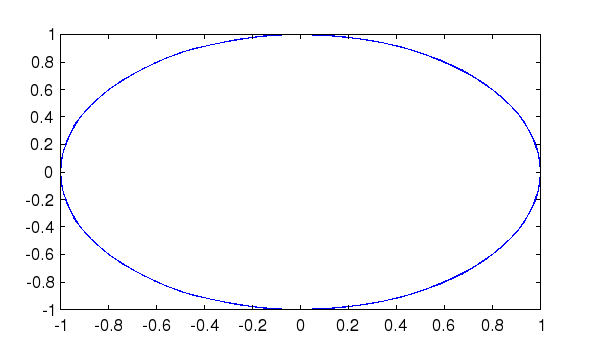
In the second example, we plot the unit circle in the
complex plane e^{i 2 pi x} for x in [-1,1].
--> x = linspace(-1,1); --> plot(exp(-i*x*2*pi))