CUMSUM Cumulative Summation Function
Section: Elementary Functions
Usage
Computes the cumulative sum of an n-dimensional array along a given dimension. The general syntax for its use isy = cumsum(x,d)
where x is a multidimensional array of numerical type, and d
is the dimension along which to perform the cumulative sum. The
output y is the same size of x. Integer types are promoted
to int32. If the dimension d is not specified, then the
cumulative sum is applied along the first non-singular dimension.
Function Internals
The output is computed via
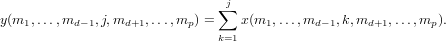
Example
The default action is to perform the cumulative sum along the first non-singular dimension.--> A = [5,1,3;3,2,1;0,3,1] A = 5 1 3 3 2 1 0 3 1 --> cumsum(A) ans = 5 1 3 8 3 4 8 6 5
To compute the cumulative sum along the columns:
--> cumsum(A,2) ans = 5 6 9 3 5 6 0 3 4
The cumulative sum also works along arbitrary dimensions
--> B(:,:,1) = [5,2;8,9]; --> B(:,:,2) = [1,0;3,0] B = (:,:,1) = 5 2 8 9 (:,:,2) = 1 0 3 0 --> cumsum(B,3) ans = (:,:,1) = 5 2 8 9 (:,:,2) = 6 2 11 9
