ANY Any True Function
Section: Elementary Functions
Usage
Reduces a logical array along a given dimension by testing for any logical 1s. The general syntax for its use isy = any(x,d)
where x is an n-dimensions array of logical type.
The output is of logical type. The argument d is
optional, and denotes the dimension along which to operate.
The output y is the same size as x, except that it is
singular along the operated direction. So, for example,
if x is a 3 x 3 x 4 array, and we any operation along
dimension d=2, then the output is of size 3 x 1 x 4.
Function Internals
The output is computed via
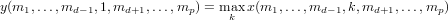
If d is omitted, then the summation is taken along the
first non-singleton dimension of x.
Example
The following piece of code demonstrates various uses of the summation function--> A = [1,0,0;1,0,0;0,0,1] A = 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1
We start by calling any without a dimension argument, in which
case it defaults to the first nonsingular dimension (in this case,
along the columns or d = 1).
--> any(A) ans = 1 0 1
Next, we apply the any operation along the rows.
--> any(A,2) ans = 1 1 1
