NDGRID Generate N-Dimensional Grid
Section: Array Generation and Manipulations
Usage
Generates N-dimensional grids, each of which is constant in all but one dimension. The syntax for its use is either[y1, y2, ..., ym] = ndgrid(x1, x2, ..., xn)
where m <= n or
[y1, y2, ..., ym] = ndgrid(x1)
which is equivalent to the first form, with x1=x2=...=xn. Each
output yi is an n-dimensional array, with values such that
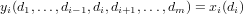
ndgrid is useful for evaluating multivariate functionals over a
range of arguments. It is a generalization of meshgrid, except
that meshgrid transposes the dimensions corresponding to the
first two arguments to better fit graphical applications.
Example
Here is a simplendgrid example
--> [a,b] = ndgrid(1:2,3:5) a = 1 1 1 2 2 2 b = 3 4 5 3 4 5 --> [a,b,c] = ndgrid(1:2,3:5,0:1) a = (:,:,1) = 1 1 1 2 2 2 (:,:,2) = 1 1 1 2 2 2 b = (:,:,1) = 3 4 5 3 4 5 (:,:,2) = 3 4 5 3 4 5 c = (:,:,1) = 0 0 0 0 0 0 (:,:,2) = 1 1 1 1 1 1
Here we use the second form
--> [a,b,c] = ndgrid(1:3) Warning: Newly defined variable nargin shadows a function of the same name. Use clear nargin to recover access to the function a = (:,:,1) = 1 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 3 (:,:,2) = 1 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 3 (:,:,3) = 1 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 3 b = (:,:,1) = 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 (:,:,2) = 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 (:,:,3) = 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 c = (:,:,1) = 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 (:,:,2) = 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 (:,:,3) = 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3
